Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on scleroderma, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
Sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim.
A composite endpoint for systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease: association with mortality in two clinical trial cohorts
Respir Res. 2025;26(1):337 DOI : 10.1186/s12931-025-03401-8
Volkmann et al. validated a composite endpoint for systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) using data from SLS II and compared performance with the SLS I cohort. The composite endpoint showed generalisability and demonstrated greater sensitivity for detecting treatment effects than forced vital capacity (FVC) alone.
Keywords:
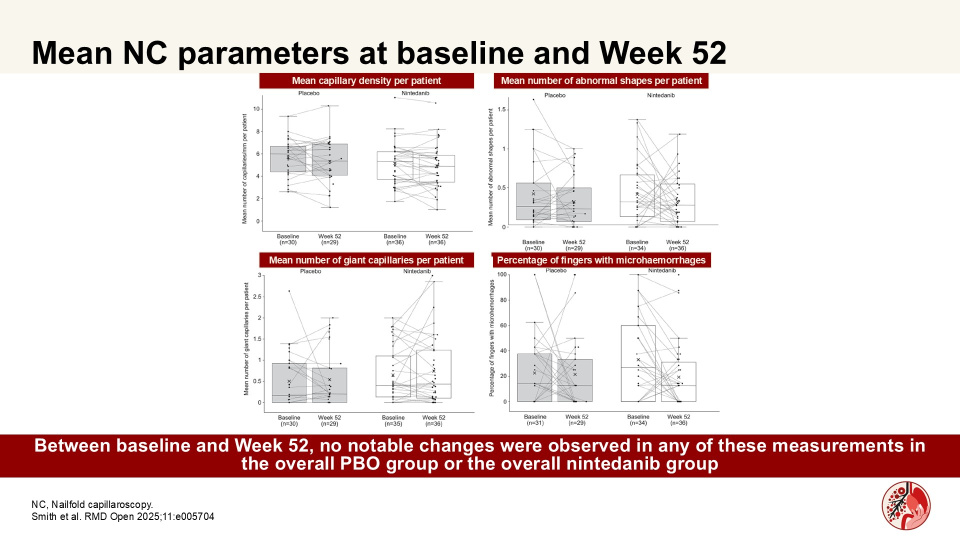
Nailfold capillaroscopy in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: A substudy of the SENSCIS trial
RMD Open 2025;11:e005704 Doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005704
In a substudy of the SENSCIS trial, Smith et al. showed that numerical differences in changes in capillary density assessed by nailfold capillaroscopy (NC) over 52 weeks may suggest a potential effect of nintedanib in patients at risk of ILD progression. Authors assessed microvascular changes in nailfold capillaries in patients with SSc-ILD who received nintedanib or PBO in a sub-study of the SENSCIS trial.
Keywords:
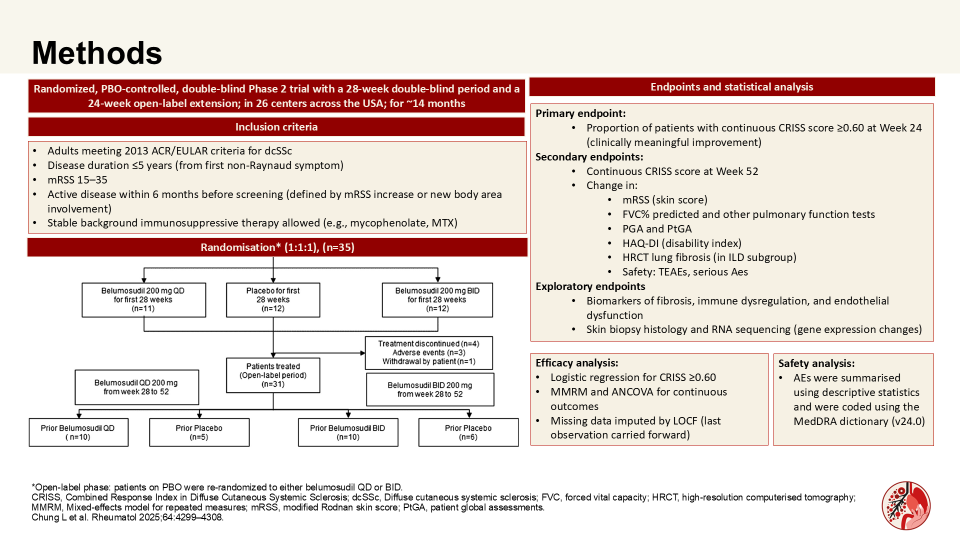
Belumosudil in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: A randomized, double-blind, open-label extension, placebo-controlled, Phase 2 study
Rheumatology 2025;64:4299–4308 Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf062
Chung et al. showed that this prematurely terminated Phase 2 trial did not identify any trend toward belumosudil efficacy as the combined response index in systemic sclerosis score (CRISS) ≥0.60 responses were similar between belumosudil and placebo groups; but it was found to have acceptable safety and tolerability. Authors evaluated the efficacy, safety and PD of orally administered belumosudil (200mg QD or BID) in patients with dcSSc.
Faecal microbiota transplantation in patients with systemic sclerosis and lower gastrointestinal tract symptoms in Norway (ReSScue): a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Lancet Rheumatol 2025;7:e323–32 doi: org/10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00334-5
Fretheim et al. showed that the faecal microbiota transplantation with ACHIM was well-tolerated in participants with systemic sclerosis but did not result in an improvement in lower GIT symptoms. Fretheim et al. compared the effects of repeated upper intestinal infusions of ACHIM with placebo in patients with systemic sclerosis and moderate-to-severe lower GIT symptoms. The ReSScue trial provides valuable insights that can inform future GIT studies in patients with systemic sclerosis.
A phase 2 randomized trial of safety and pharmacokinetics of IgPro20 and IgPro10 in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis
Rheumatology 2025;64:3657–66 doi: org/10.1093/rheumatology/keaf066
Denton et al. showed that SC administration of immunoglobulin is generally well-tolerated in patients with dcSSc. Denton et al. evaluated the safety of IgPro20 in adults with dcSSc by recording of AEs, TEAEs, AE of special interests, ISRs and associated clinical tests. The secondary objectives were assessing PK and relative bioavailability of IgPro20, and the safety profile and PK of IgPro10. The ISR rate was low with no severe or serious TEAEs affecting the skin reported, despite moderate-to-severe skin involvement in all subjects and pathological skin features. Overall safety, PK and bioavailability profiles of IgPro20, and safety and PK of IgPro10 were similar to those observed in other indications.
Nintedanib for systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease
N Engl J Med 2019;380:2518–28 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1903076
Distler et al. reported that the annual rate of decline in FVC through Week 52 was lower with nintedanib than with placebo among patients with ILD associated with SSc. No clinical benefit of nintedanib was observed for other manifestations of SSc. The safety profile of nintedanib was similar to that observed in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords:
EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis: 2023 update
Ann Rheum Dis 2025;84:29–40 DOI: 10.1136/ard-2024-226430
Del Galdo et al. formed a new task force to update the EULAR recommendations for the pharmacological management of systemic sclerosis (SSc). The task force agreed on 22 new recommendations covering eight clinical/organ domains: Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP), digital ulcers, pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), musculoskeletal, skin fibrosis, interstitial lung disease (ILD), gastrointestinal, and renal crisis.
Keywords:
Comparative efficacy of immunosuppressive therapies in the treatment of diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis
ACR Open Rheumatol 2025;7:e70004 DOI: 10.1002/acr2.70004.
White et al. report a post hoc analysis of the RESOLVE-1 trial comparing immunosuppressive therapies in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc), finding numerically greater improvement in modified Rodnan skin score and stabilisation of lung function with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), particularly in patients with early-stage disease and anti–topoisomerase 1 antibodies. These findings strongly support MMF as a preferred background therapy in this population.
Keywords:
Tocilizumab in systemic sclerosis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 trial
Lancet Respir Med 2020;8:963–74 DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30318-0.
Khanna et al. evaluated tocilizumab in patients with early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis in the focuSSced trial. The primary endpoint of improved skin fibrosis was not met, but a key secondary outcome showed that tocilizumab significantly preserved lung function compared with placebo.