Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on scleroderma, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
Sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim.
Nailfold capillaroscopy in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: A substudy of the SENSCIS trial
RMD Open 2025;11:e005704 Doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005704
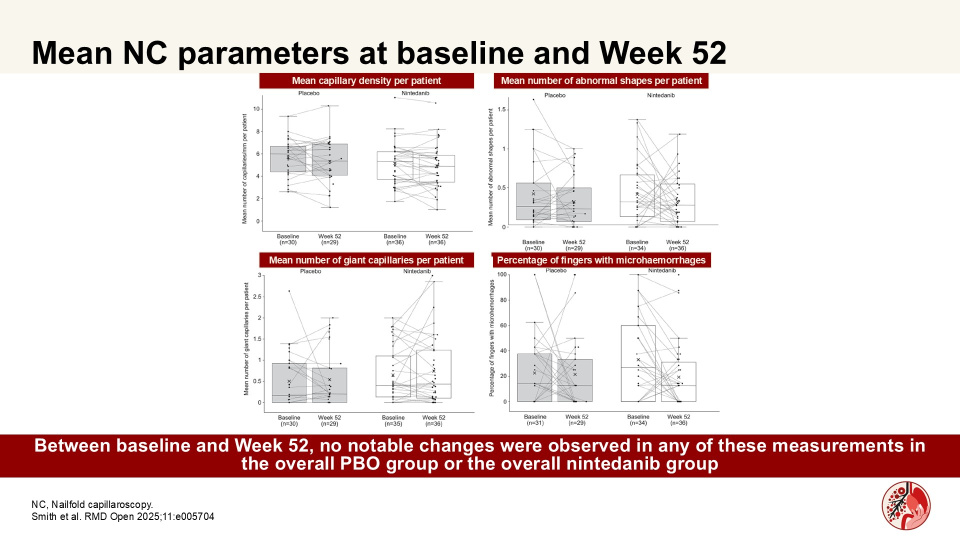
In a substudy of the SENSCIS trial, Smith et al. showed that numerical differences in changes in capillary density assessed by nailfold capillaroscopy (NC) over 52 weeks may suggest a potential effect of nintedanib in patients at risk of ILD progression. Authors assessed microvascular changes in nailfold capillaries in patients with SSc-ILD who received nintedanib or PBO in a sub-study of the SENSCIS trial.
Keywords:
EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis: 2023 update
Ann Rheum Dis 2025;84:29–40 DOI: 10.1136/ard-2024-226430
Del Galdo et al. formed a new task force to update the EULAR recommendations for the pharmacological management of systemic sclerosis (SSc). The task force agreed on 22 new recommendations covering eight clinical/organ domains: Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP), digital ulcers, pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), musculoskeletal, skin fibrosis, interstitial lung disease (ILD), gastrointestinal, and renal crisis.
Keywords:
Nintedanib for systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease
N Engl J Med 2019;380:2518–28 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1903076
Distler et al. reported that the annual rate of decline in FVC through Week 52 was lower with nintedanib than with placebo among patients with ILD associated with SSc. No clinical benefit of nintedanib was observed for other manifestations of SSc. The safety profile of nintedanib was similar to that observed in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.